Natural EVs in cancer therapy. a) TEX stimulate immune activation by
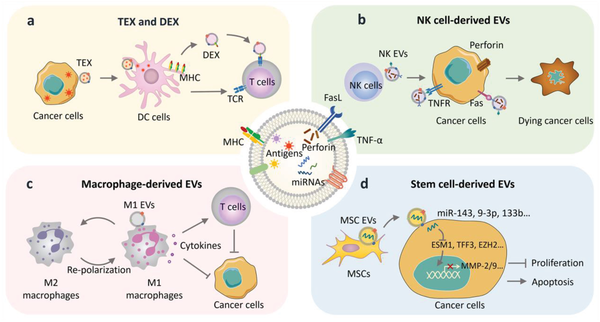
Download scientific diagram | Natural EVs in cancer therapy. a) TEX stimulate immune activation by boosting T‐cell expansion and function via APCs especially DC cells. DEX activate T cells by mimicking the role of APCs. b) NK‐cell‐derived EVs induce tumor cell death through FasL, perforin, and TNF‐α. c) EVs from M1 macrophages can re‐educate tumor associated macrophages from M2 to M1 phenotype, which further activates anti‐tumor immunity. d) Stem‐cell‐derived EVs inhibit the growth of tumor cells through miRNA‐mediated mechanisms. Abbreviations: DC cell, dendritic cell; DEX, dendritic cell‐derived EVs; FasL, Fas ligand; M1 EVs, M1 macrophage‐derived EVs; MHC, major histocompatibility complex; MSCs, mesenchymal stem cells; NK EVs, NK cell‐derived EVs; TCR, T cell receptor; TEX, tumor cell‐derived EVs; TNF‐α, tumor necrosis factor‐α; TNFR, tumor necrosis factor receptor. from publication: Engineered Extracellular Vesicles for Cancer Therapy | Extracellular vesicles (EVs) have emerged as a novel cell-free strategy for the treatment of many diseases including cancer. As a result of their natural properties to mediate cell-to-cell communication and their high physiochemical stability and biocompatibility, EVs are | Extracellular Vesicles, Cancer Therapy and Bioinspired | ResearchGate, the professional network for scientists.
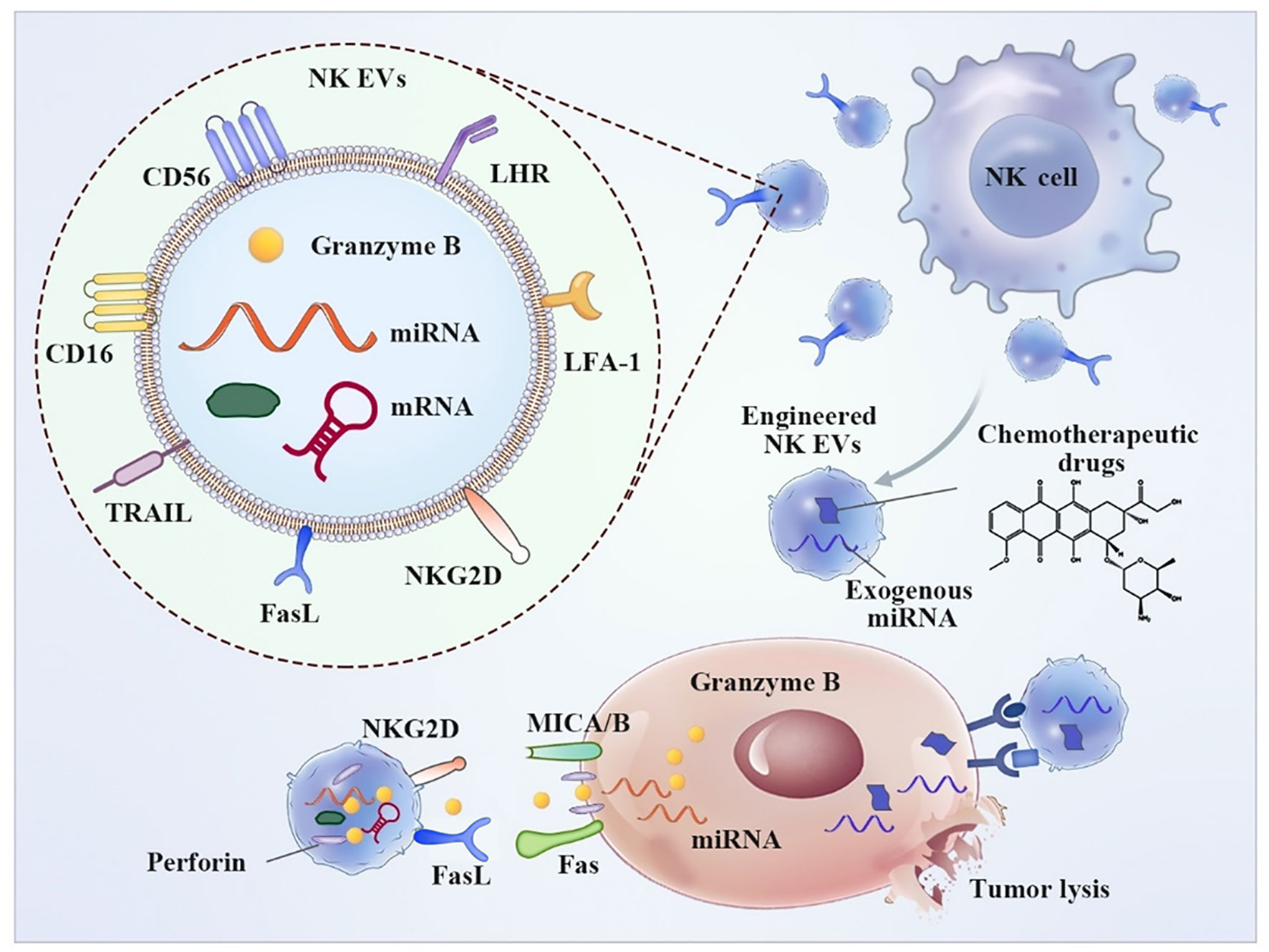
Frontiers Immune Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles – New Strategies in Cancer Immunotherapy

Extracellular Vesicles in Cancer Immune Microenvironment and Cancer Immunotherapy - Xie - 2019 - Advanced Science - Wiley Online Library

Cancer immunology - Wikipedia

Anticancer Therapy Targeting Cancer-Derived Extracellular Vesicles
Role of extracellular vesicles in osteosarcoma

An immune score reflecting pro- and anti-tumoural balance of tumour microenvironment has major prognostic impact and predicts immunotherapy response in solid cancers - eBioMedicine

Extracellular vesicles from triple negative breast cancer promote pro-inflammatory macrophages associated with better clinical outcome

Extracellular vesicles and oncogenic signaling - Schubert - 2021 - Molecular Oncology - Wiley Online Library

Extracellular vesicle–based drug delivery in cancer immunotherapy

Molecules boosting plant immunity identified
Extracellular vesicles as a next-generation drug delivery platform









